What is an Operator?
A Kubernetes Operator is a software component that extends the Kubernetes platform to manage specific types of applications and their underlying infrastructure. Operators provide a high-level and abstract way to manage the entire application stack, including deployment, scaling, upgrades, and maintenance of the application components. By encapsulating the operational knowledge of a specific application into a reusable package, operators simplify the deployment and management of complex applications within a Kubernetes environment.
Operators are custom controllers that watch the changes in the state of the application and take necessary actions to keep the application running as expected, providing a declarative interface for managing the application and ensuring a desired state is achieved. Kubernetes natively doesn’t have the knowledge required to automate the process of deploying every single stateful application, Operator custom CRD’s will extend Kubernetes API to overcome this issue.
Prometheus Operator:
The Prometheus Operator is a software component that extends the Kubernetes platform to manage Prometheus, an open-source monitoring and alerting system. The Prometheus Operator provides a simple and easy way to deploy, configure, and manage Prometheus instances within a Kubernetes cluster.
Why Prometheus Operator?
With the use of Prometheus Operator, users can automate the deployment and management of Prometheus instances, reducing the time and effort required to configure and maintain monitoring for their applications. The Prometheus Operator also provides built-in support for features such as rolling updates, scaling, and backup and restore, making it easier for users to ensure that their monitoring systems are reliable and scalable.
Why Observability and Monitoring?
Monitoring focuses on predefined metrics to identify when a specific platform or application is performing within expectations. The metrics tracked generally focus on things like resource utilisations.
Observability combines metrics, logs and traces a specialised form of logging to instrument applications in a way that makes it simpler to troubleshoot issues without having to rely solely on a limited set of metrics that have been pre-defined to monitor a specific process or function. Observability provides proactive prevention with the help of collected metrics.
Prometheus Architecture:
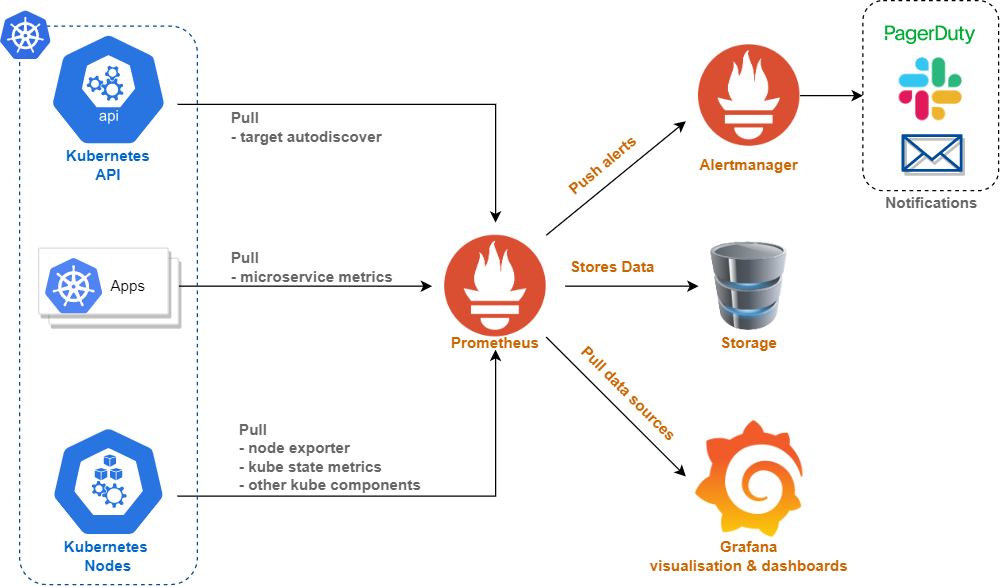
Setting Up Prometheus Helm Operator:
Deploying Prometheus Operator and kube-prometheus in an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster using Prometheus operator Helm.
- Pre-Requisites:
- Azure Account
- AKS Cluster
- Install Azure CLI
- Get the Kube Context file
- Install Helm package
- To add the Prometheus chart repository to Helm, utilise the following command:
$ helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts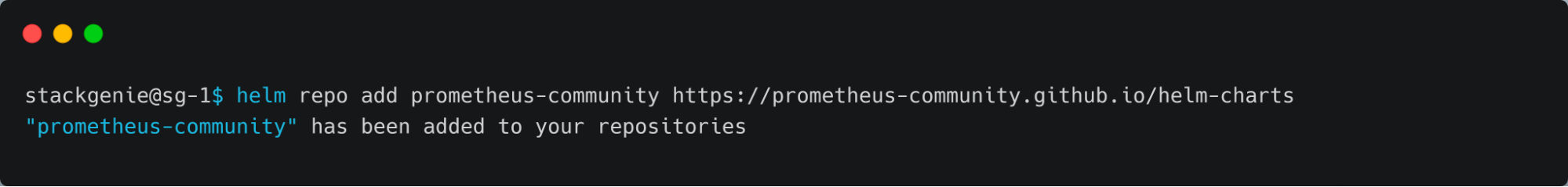
- Install the Prometheus Operator Helm chart onto the AKS Cluster:
- Login to the Grafana dashboard and retrieve Prometheus metrics:
- Login to the Grafana dashboard and retrieve Prometheus metrics:
- Login to the Grafana dashboard and retrieve Prometheus metrics:
- Login to the Grafana dashboard and retrieve Prometheus metrics:
- Use the “helm list” command to display a list of deployed Helm charts:
- Access the localhost using the designated port number on your browser.
Conclusion:
In a nutshell, deploying the Prometheus Operator to monitor Kubernetes clusters using Helm is a straightforward process. Helm allows us to easily install, upgrade, and manage the Prometheus Operator and its components, including Alertmanager and Grafana, with just a few simple commands. By following the steps outlined in this blog, you can quickly deploy and configure the Prometheus Operator, and start collecting and visualising metrics for your Kubernetes clusters. With the Prometheus Operator, you can gain valuable insights into your clusters’ health and performance, and make informed decisions to optimise their performance and reliability.
Are you looking for expert guidance on your infrastructure or DevOps implementation strategy? Contact Stackgenie to find out how we can help your operations reach the next level.


